Navigating the Future of Healthcare Apps: The Critical Role of EDI in Digital Healthcare
Healthcare
As technology continues to play an increasingly significant role in healthcare, from providers to insurers to patients, the need for efficient data exchange has never been greater. This is where Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) comes into play. EDI is a fundamental component in modern healthcare applications, enabling the secure and efficient transfer of data. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of EDI in healthcare, its impact on developing healthcare applications, and how it shapes the future of data exchange in medicine.
EDI for Healthcare Web and Mobile Apps
EDI in the context of healthcare apps, can be defined as the exchange of structured data between systems by using predefined formats. It makes it possible for healthcare providers, insurers, and other stakeholders to exchange information in a more efficient manner and with little to no intermediaries in the form of paper documents.
EDI Process For Web And Mobile Applications
1. Standardized Data Formats:
EDI uses standards like X12 which is a standard that was developed by the Accredited Standards Committee (ASC) and is effective in enforcing structures and contents of the data used in the different systems.
2. Data Translation and Mapping:
EDI systems are used to translate data in an organization’s internal format to the format used by EDI and vice versa. This is known as mapping so that information is understood in the same way by different systems.
3. Data Transmission Protocols:
EDI utilizes systems such as AS2 or SFTP to guarantee the secure transfer of health information.
4. Data Validation and Processing:
Once the EDI data arrives at the receiving party, it undergoes a series of validation checks. These checks ensure that the data is accurate, complete, and meets the required standards. Only after passing these validations is the data processed and integrated into the recipient’s system.
Advantages of Implementing EDI in Healthcare Applications
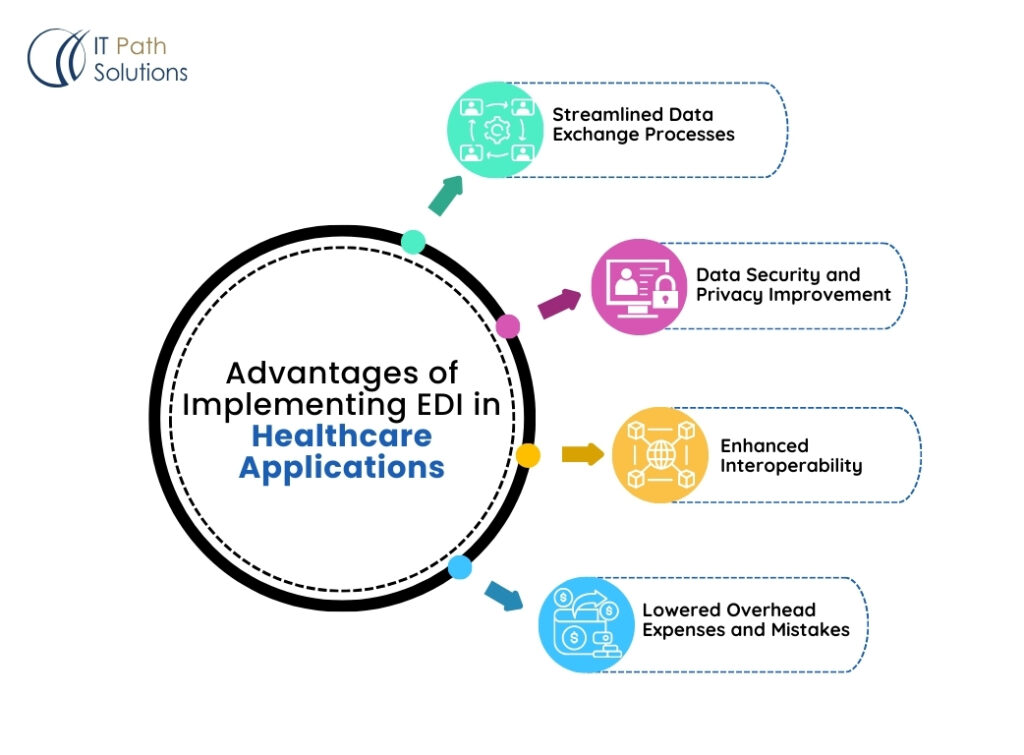
1. Streamlined Data Exchange Processes
EDI automatically eliminates the need for manual entry of data and is therefore a very effective means of cutting down the time that is used to process data. This results in quicker processing of claims, additionally cloud computing for healthcare is very popular for maintaining databases, retrieving information on patients, eligibility checks, and other healthcare activities that are so vital in today’s healthcare environment.
2. Data security and privacy improvement for the healthcare business (HIPAA compliance)
EDI systems include strong measures of security to enhance the protection of the patient’s data during transfer and storage. This is important for the firm to meet the HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) requirements.
3. Enhanced Interoperability between Health Facilities
EDI is beneficial for the exchange of data in healthcare since it allows using the same format regardless of the underlying technology. Such compatibility is crucial in the provision of health care services since it leads to better coordination in the management of patient care.
4. Lowered Overhead Expenses and Mistakes
EDI also eliminates the need for manual data entry and paper-based processes, which helps reduce costs for healthcare organizations. Additionally, this type of software typically falls within a medium price range, making it a cost-effective solution for managing healthcare organizations. Additionally, it minimizes the risk of errors that can occur due to human involvement.
Key Considerations for EDI Integration in Healthcare App Development
1. HIPAA and Other Health Care Standards and Guidelines
While implementing EDI in healthcare applications, the developers should follow the HIPAA rules and other healthcare regulations. Developers also develop EHR software development, it’s generally used for Health and medical data in the system This entails putting measures in place to ensure the protection of data and ensuring that all data exchanges are recorded.
2. Secure Data Transmission Protocols
AS2 or SFTP is used for the transmission of secure data in the healthcare sector because the data is sensitive and requires protection during the transfer. These protocols offer the means for encrypting or authenticating the data so that it cannot be intercepted or modified by an unauthorized party.
3. RBAC and User Authentication
Mandatory user authentication and proper authorization of the users is an essential step to guarantee that only those who are allowed can both view and manipulate the EDI data in the healthcare application.
4. Encrypted Communication Channels
It is recommended that all the communication links employed in the EDI transactions should be protected from unauthorized access by being encrypted.
EDI Transaction Types in Healthcare Applications
Mobile healthcare applications have revolutionized the management and exchange of medical data. At the heart of this transformation is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), a crucial method for securely transmitting information among healthcare providers, insurers, and other stakeholders using electronic media. A common feature among most healthcare apps is their ability to handle various types of EDI transactions, each serving a unique function within the broader healthcare ecosystem. These transactions streamline communication, enhance data accuracy, and improve overall efficiency in healthcare delivery.
1. Healthcare Claim Transactions (837)
These transactions are used in the conversion of claims for health care services into electronic form and submission to insurers. The 837 transaction set is crucial for efficient billing processes and comes in three main varieties: The 837 transaction set is crucial for efficient billing processes and comes in three main varieties:
- 837P: for Professional claims (for example, services of a physician)
- 837I: for Institutional claims, for example, Inpatient and Outpatient services.
- 837D: for Dental claims
With the help of 837 transactions, the possibilities of paperwork reduction, error elimination, and the acceleration of the reimbursement process are possible. This results in better cash management and fewer expenses incurred in the management of the business.
2. This code deals with inquiries concerning eligibility and benefits in the 270/271 system.
These transactions allow hospitals and other care facilities to verify the insurance and the specifics of the patient in real-time. The process involves:
- 270 transaction: The provider submits a query about a patient’s insurance status.
- 271 transaction: The insurer promptly provides information on the patient’s coverage status and the available coverage amount.
This real-time confirmation assists in eliminating instances where a claim is denied due to eligibility and helps the healthcare providers explain the financial responsibility of the patient before the service delivery. It also enhances the check-in process and the level of satisfaction among the patients.
Streamline your revenue cycle with EDI in healthcare. Schedule a doctor appointment by application today and start your journey toward an efficient solution.
3. These are the claim status requests and notifications through either code 276 or 277.
Such transactions enable providers to check the status of the filed claims and get information from the insurers. This process involves:
- 276 transaction: In response to the request for claim status, the provider receives a response.
- 277 transaction: The insurer comes back with the status of the claim as it is at the time of the response.
Such transactions help providers monitor the claims through the adjudication process, to detect and solve the problems as soon as possible, and control the accounts receivable. Since phone calls and manual follow-up are eliminated, 276/277 transactions are efficient for both the provider and insurer.
4. Other Relevant Transaction Types
Depending on the specific needs of the healthcare app, other EDI transaction types may include: Depending on the specific needs of the healthcare app, other EDI transaction types may include:
- Remittance advice (835) for payment details: This transaction gives the amount of payment made, the charges made, the adjustments made if any, and the reasons for any denial. It facilitates the process of posting payments and reconciling the accounts on an automatic basis.
- Authorization and referral request (278): This was employed to seek permission for specific medical interventions or to refer a patient to a specialist. This transaction assists in guaranteeing that services are paid for before they are rendered hence minimizing the instances of claim rejections.
- Health care service review (278): Like the authorization request, this transaction is used for utilization review to verify that the suggested treatments are reasonable and necessary.
Additional EDI transaction types that may be incorporated into healthcare apps include: Additional EDI transaction types that may be incorporated into healthcare apps include:
- Enrollment/disenrollment in a health plan (834): Employer or sponsor’s tool to include or exclude a person into or from the health insurance plan.
- Functional acknowledgment (997): Acknowledges that an EDI transmission was sent and received by the intended recipient in its entirety.
- Payment order/remittance advice (820): Used for digital fund transfer, which is frequently linked to the 835 transaction.
- Benefit enrollment and maintenance (834): Enables the exchange of benefit enrollment details electronically between the sponsors and the insurers.
With the help of these several types of EDI transactions, healthcare applications can effectively minimize administrative work, eliminate errors, and bring better cash flow and patient care. With the advancement in technology like generative AI in healthcare and the increase in the use of electronic platforms in the healthcare industry, the efficiency of EDI transactions in healthcare applications cannot be overemphasized.
Best Practices for Developing EDI-Compliant Healthcare Apps
1. Selecting the Right EDI Solution/Provider
EDI partnership or solution selection is a critical success factor when it comes to integration. Some of the things to look at when making this decision include; scalability, compliance certifications, and transaction types that are relevant to the healthcare industry.
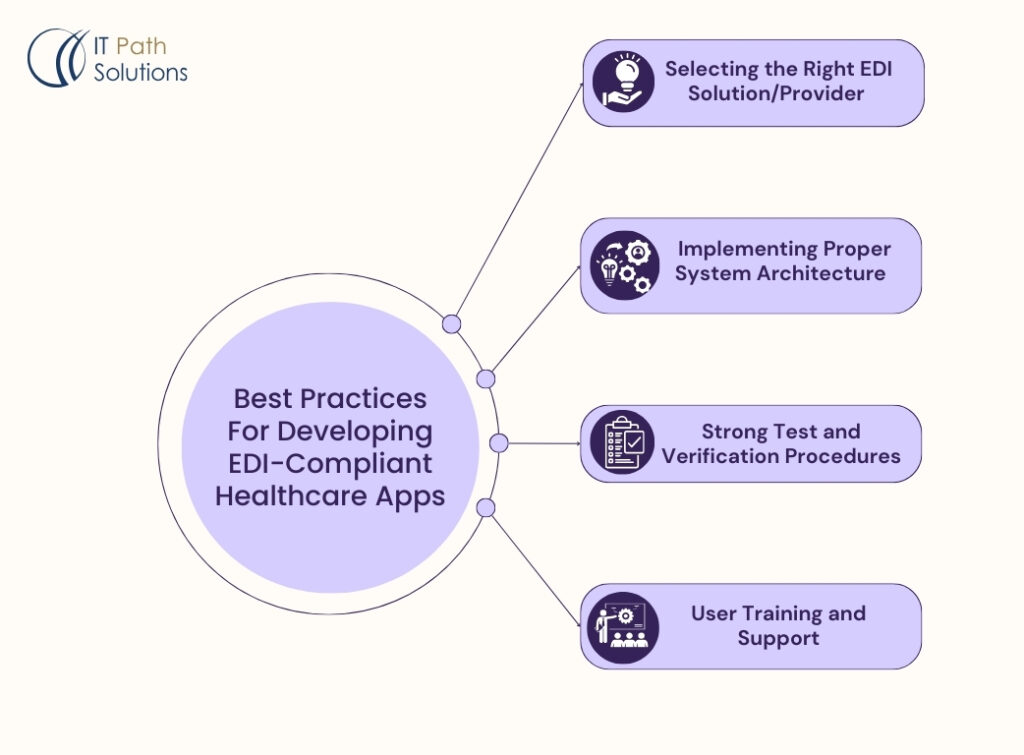
2. Implementing Proper System Architecture
Consider the app’s architecture and plan for the efficient processing of EDI transactions and growth. This may include things like message queueing, load balancing, and other architectural patterns to handle large volumes of EDI data.
3. Strong Test and Verification Procedures
Use a range of testing processes to ensure the EDI transactions are correct at different levels, such as at the format level, content level, and trading partner level.
4. User Training and Support
Make sure that those who are going to use the EDI-enabled healthcare app receive enough training and one-on-one support. This entails developing comprehensible documentation, providing the users with guidelines, and ensuring they have adequate technical support in case of any complications.
EDI and Its Future in Healthcare App Development
Emerging Trends and Technologies
As healthcare technology continues to evolve, several trends are shaping the future of EDI integration in healthcare apps: As healthcare technology continues to evolve, several trends are shaping the future of EDI integration in healthcare apps:
1. API-based EDI:
EDI transactions are moving more to APIs as the type of transactions that offer more flexibility and real-time transfers. This strategy is highly compatible with the increasing use of mHealth, which makes it possible to incorporate the EDI functionality into various mobile health applications.
2. Blockchain for EDI:
EDI is one of the significant applications that is implemented in the sphere of healthcare where the idea of applying blockchain technology as a solution is discussed to enhance the level of security and transparency concerning the transactions. This could go a long way in improving HIPAA compliance.
3. AI and Machine Learning:
They are being employed to improve the facets of data mapping and validation as well as processing in EDI systems. They can also enhance HL7 Integration which will enhance the process of transferring health information from one system to another.
4. Cloud-based EDI Solutions:
EDI services are also frequently deployed on the cloud to meet the required scalability while incurring minimal infrastructure expenses for healthcare organizations. This approach fosters the development of TeleHealth since it allows for the access of EDI services from different devices and places.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
While the future of EDI in healthcare app development is promising, several challenges need to be addressed While the future of EDI in healthcare app development is promising, several challenges need to be addressed:
1. Evolving Regulatory Landscape:
They have to be so because the regulations of the healthcare systems remain dynamic and hence, the EDI systems and apps must be equally dynamic. Further, some compliance checks and updates will require to be done more often than others. This is especially important when dealing with issues that are strictly regulated by HIPAA, given that the regulations are constantly evolving.
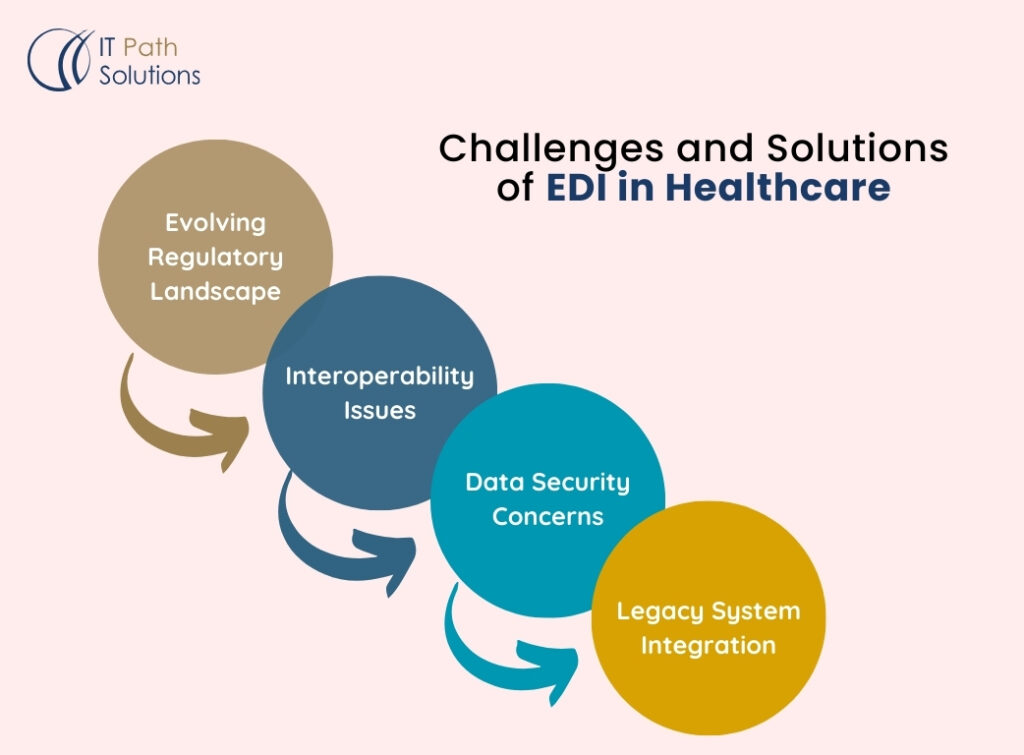
2. Interoperability Issues:
Despite efforts towards standardization, the issue of compatibility remains unresolved. However, further standardization work and the adoption of free-form data sharing standards like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) could help address these challenges. Enhanced HL7 integration capabilities can also play a crucial role in effectively overcoming interoperability issues.
3. Data Security Concerns:
This means that although the amount of electronic health data exchange is expected to increase, maintaining sufficient security will remain a persistent challenge. The suggestions made include the use of complex encryption methods and the security scans should be conducted frequently. This is especially true for mHealth applications, as such applications generally deal with personal patients’ information on mobile gadgets.
4. Legacy System Integration:
At present, the majority of healthcare organizations employ outdated and inefficient systems and, therefore, they have problems with EDI integration. The solution to this challenge will therefore entail the creation of good middleware solutions and migration plans. HL7 Integration best practices can assist in transitioning from old monolithic systems to new EDI systems.
Conclusion
The integration of EDI into healthcare web and mobile applications significantly improves data exchange efficiency, security, and standardization. These EDI-enabled apps are essential for future healthcare delivery, facilitating process integration, system interoperability, and HIPAA compliance. By staying updated with mHealth trends and ensuring robust HL7 integration, the healthcare industry can enhance patient care, reduce paperwork, and create a more connected and efficient system.
 Healthcare
Healthcare  Education
Education  Real Estate
Real Estate  Logistic
Logistic  Fitness
Fitness  Tourism
Tourism  Travel
Travel  Banking
Banking  Media
Media  E-commerce
E-commerce